Mechanisms Within The Java Full Stack Development
- k4666945
- 2 days ago
- 3 min read

Introduction
Java full stack development combines client-side and server-side technologies to produce entire web apps. Database administration, back-end logic, and front-end design management all fall under this. Scalable and interactive systems are produced by developers using Java, Spring Boot, and contemporary frameworks. By ensuring perfect interaction across all levels, this method offers efficient, reactive, and safe applications. Learn front-end, back-end, and database development with real-time project experience by enrolling in a Java Full Stack Course.
All About Java Full Stack Development
Java Full Stack Development is working on both front-end and back-end web applications. Responsive user interfaces are created by Java full stack developers; they also run databases and servers. For front end work, they employ HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are used for front end tasks. Hibernate, Spring Boot, and Java are used for the back end.
The developer uses databases including MySQL and MongoDB. With REST APIs, they know how to connect the server and client. Their goal is to create effective, scalable, and safe programs. Applications are put into production environments and tested, debugged. To simplify development, they frequently employ tools such Git, Jenkins, and Docker.
Good framework knowledge and problem-solving abilities are needed for this role. Strong job chances abound throughout sectors thanks to Java Full Stack Development. Still among the most sought-after areas in the field of software development today.
Mechanisms Within The Java Full Stack Development
Java Full Stack Development comprises creating whole web applications with client-side as well as server-side elements. Technologies managing databases, application logic, and user interfaces are integrated here. Every level in the stack has clear protocols to speak by. The process guarantees performance, scalability, and seamless data flow.
Front-End Mechanism:
Handling the user interface in Java Full Stack Development is the front-end mechanism. Designs and structures web pages with tools including JavaScript, HTML, CSS. Interactive elements are created with React or Angular among other frameworks. HTTP queries let the browser send user inputs to the server; front-end code is run.

AJAX helps front-end developers to get information asynchronously from the back-end. Avoiding full page reloads improves user experience with this technique. Data interchange is achieved by the front end speaking with RESTful APIs. It dynamically modifies the DOM and processes JSON responses.
Back-End Mechanism:
Java Full Stack Development's back end handles the application logic, authentication, and corporate rules. Spring Boot helps Java developers to construct RESTful APIs. The server replies on front end requests, contacts the database, and processes those requests. The system guarantees that every customer request is answered logically.

The Spring Boot framework streamlines dependency management and deployment. Used by the back end, POJOs (plain old Java objects) oversee data models and CRUD operations; hand requests comprise tags like @RestController, @GetMapping, and @PostMapping. Get actual experience with Spring Boot, React, and sophisticated deployment techniques by registering in the Java Full Stack Developer Course in Hyderabad.
Database Mechanism:
Beginning with the database mechanism, data persistence in Java Full Stack Development sees developers utilize non-relational ones like MongoDB or relational ones such MySQL. Java uses Hibernate and JPA (Java Persistence API) to map items to database tables. The system lets CRUD activities be done without complicated SQL queries written.
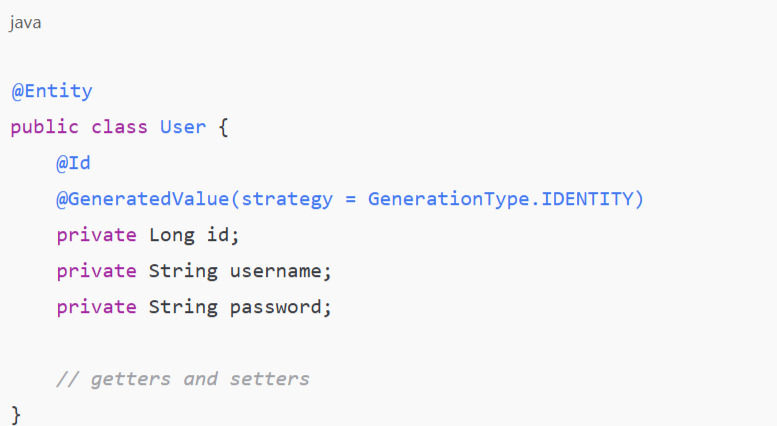
Entity classes are database tables' substitutes. Hibernate turns entity actions into SQL statements connecting to the database. This process promotes transactions and preserves data integrity.
Integration Mechanism:
Integration links the database, back-end, and front-end levels. The mechanism of communication is restful APIs. The client sends HTTP requests; the server answers in XML or JSON. The integration method guarantees safe and effective data transfer.

Spring Boot exposes endpoints via controllers. Fetch() or axios is used by the front-end to call these APIs. Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) rules solve queries from several domains. This assures perfect data transfer between the server and the browser.
Deployment Mechanism:
The deployment method lets users access the Java Full Stack application. Continuous integration and deployment tools for developers include Docker, Jenkins, and AWS. A servlet container like Tomcat runs the back end. One can use the front end on a CDN or cloud platform.
Jenkins manages the building process automatically; Docker containers guarantee uniform environments. The system guarantees version control, load balancing, and scalability.
Conclusion
Responsive, safe, and scalable web applications result from the synergy of the processes in Java Full Stack Development. Every level uses logic, request processing, and data management in a particular way. Develop scalable enterprise-level web applications with the Java Full Stack Developer Course in Pune to advance your career. Combining front-end, back-end, and database operations guarantees flawless connection. Technologies like Spring Boot and Hibernate let developers produce efficient enterprise-grade systems meeting modern application needs.



Comments